- Details
- Hits: 2296

Okinawa, Japan. (December 8, 2024): Who came up with the ridiculous idea of two groups of people on opposite ends of a rope pulling against each other? In this photo by Lance Corporal Aaliyah Hunt, Marines and Sailors compete in a tug-of-war contest, a “game” that dates back centuries.
Historians say the game originates from ancient ceremonies and cults in Egypt, Burma, and India and similar contests appeared in Japan, Korea, Hawaii, and South America. The earliest evidence of the tug of war in Western Europe is around 1000 AD in Scandinavia and Germany in what were called “power games.” Tug of war contests can even be traced to the courts of Chinese Emperors in Mongolia and Turkey.
Today’s tug of war community is serious about the sport and there are rules. Tug-of-war contests are held between two teams of eight competitors and the rope must be forty yards long exactly. The Judge (yes, one is required) issues three commands, “Pick up the rope,” “Take the string,” and finally “Pull.” The contest is decided by the best two out of three pulls.
- Details
- Hits: 3204
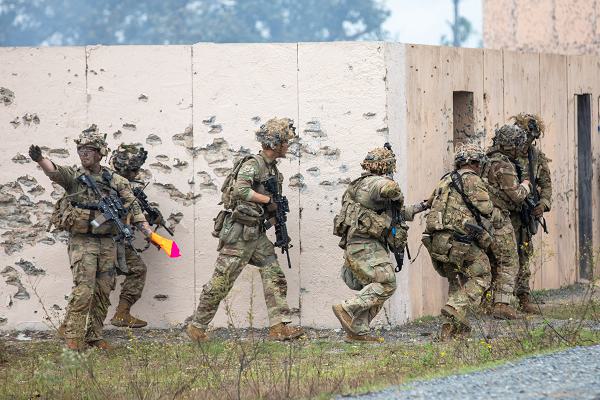

Fort Johnson, Louisiana. (December 13, 2024): Close Quarter Battle or CQB, is when an infantry Soldier gets “up close and personal” with the enemy in brutal, chaotic combat. In this photo by Specialist Isaiah Mount, Soldiers prepare to breach and clear a house during a live-fire exercise at the Joint Readiness Training Center here. The assault team practiced rapidly entering a building using force and momentum to overwhelm any threats inside. The team moves with “controlled aggression” to quickly dominate and clear each room of combatants. It is tough work characterized by sudden violence at close range.
This type of combat has occurred since the beginning of warfare. The ancients used lances or swords in individual combat, Allied Soldiers resorted to bayonets during trench warfare in World War I, and close quarter combat was developed into a science in World War II.
The concept of CQB, also known as Defendu, was a new form of martial arts developed by William E. Fairbairn and Eric A. Sykes, both former British Soldiers and police officials in Shanghai, China prior to World War II. The new tactics involved using firearms to assault structures while minimizing friendly casualties. The program stresses surprise, speed, and controlled violent action with each playing a critical role in the success of an assault.
- Details
- Hits: 1547
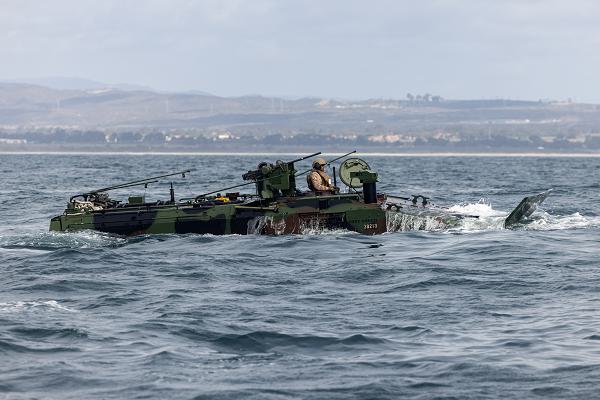

Camp Pendleton, California. (December 9, 2024): After overcoming initial obstacles, the Marine Corps is currently deploying its new Amphibious Combat Vehicle (ACV) to bases in Japan, Guam, and the Philippines. In this photo by Corporal Kyle Chan, a Marine guides this next generation amphibious craft toward shore during exercises with the 1st Marine Division. The ACV deployment is part of an overall refocusing of strategy to confront China in the Indo-Pacific.
Under this new plan, the Marines would rapidly deploy to remote islands to operate in smaller, more dispersed groups. This is a challenging logistical task given the size of the Indo-Pacific. The goal is to field a highly dispersed force capable of conducting amphibious operations independently with the least amount of logistical support.
The new ACV offers greater mobility and has many improvements in fire power and personnel protection. Manufactured by BAE Systems, the ACV is an eight-wheel craft launched and recovered from ships in open water that can carry up to thirteen Marines. The new design has improved survivability with a blast-resistant hull, energy absorbing seats, and an automatic fire suppression system. Its V-shaped frame further reduces the risk to its occupants from mines and improvised explosive devices.
- Details
- Hits: 1732
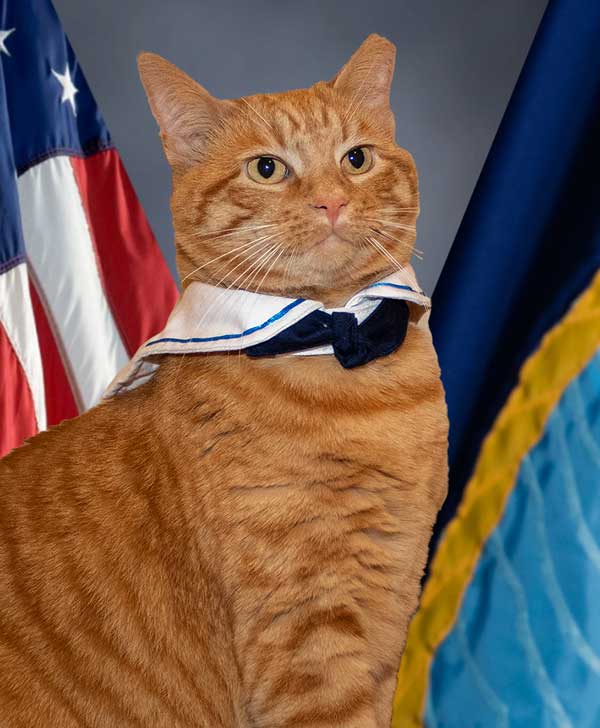

Tokyo, Japan. (December 15, 2024): In this photo by Petty Officer 2nd Class Ashley Cheesman, Cracker Jack the Sailor Cat proudly sports his Navy garb to celebrate International Cat Day. America’s Sailors have a long and mutually beneficial relationship with cats. Cracker Jack the Sailor Cat is a character celebrated by sailors for the historical role cats served on ships. Boxes of Cracker Jacks featured a Sailor and his dog in the 1920 and American mariners began calling their uniforms “cracker jacks.”
For centuries, Ships’ cats were a vital part of the crew by helping to keep their mutual home free of rats and other vermin. They were also known for their ability to sense changes in barometric pressure, helping crews predict storms.
Rats can cause damage to ropes, woodwork, and electrical wiring and they were a threat to ships' stores, devouring crews' food, and cargo. They were also a source of disease as rat fleas carried plague and are believed to be the source of the ghastly Black Death.
- Details
- Hits: 1294

Twentynine Palms, California. (December 6, 2024): As the saying goes, bureaucracies strangle innovation. To cut through the red tape, the Defense Department has created an agency to accelerate the process of absorbing new technologies, in this case drones. In this photo by Devon Bistarkey, the Defense Innovation Unit is using drone operators and experts to field test, evaluate, and accelerate the adoption of commercial technology by the military. The Agency holds periodic “Challenges” like these to allow companies to compete by demonstrating their latest innovations to the Military.
These Innovation Unit team Challenges attract drone operators and test experts of various uncrewed aerial systems from all over the world. The purpose of this event was to directly evaluate Unmanned Aerial System platforms and assess rapid-update software. If selected, the approved drones may join the UAS list for rapid deployment.
- Details
- Hits: 3835
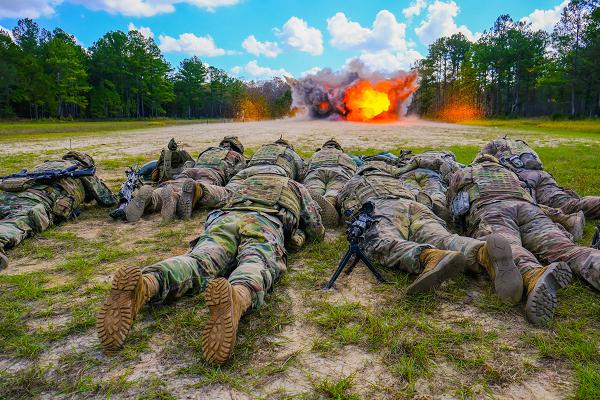

Fort Stewart, Georgia. (November 28, 2024): In this photo by Sergeant Anthony Ford, soldiers take cover as a Bangalore torpedo explodes just to their front. This famous device is credited with saving thousands of allied lives on D-Day. The Bangalore was originally designed by local farmers wanting to clear paths and heavy undergrowth. Along comes Captain R. L. McClintock of the Royal Engineers in 1912 who created a more powerful explosion and a whole new role for the Bangalore.
Soon, use of the “Bangalore” mine would sweep through the British Army and it quickly became the primary tool used by combat engineers. The device saved lives by allowing troops to clear obstacles that would otherwise require them to approach directly, possibly under fire. The mine originally looked something like a long chimney brush with an explosive charge attached and then several connected tubes added to the required length.